Page 20 - Fall2010
P. 20
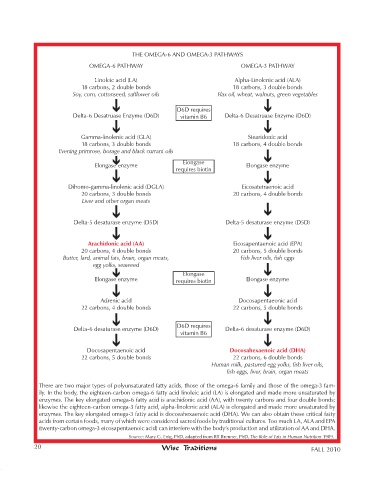
THE OMEGA-6 AND OMEGA-3 PATHWAyS
OMEGA-6 PATHWAy OMEGA-3 PATHWAy
Linoleic acid (LA) Alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA)
18 carbons, 2 double bonds 18 carbons, 3 double bonds
Soy, corn, cottonseed, safflower oils Flax oil, wheat, walnuts, green vegetables
D6D requires
Delta-6 Desatruase Enzyme (D6D) vitamin B6 Delta-6 Desatruase Enzyme (D6D)
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) Stearidonic acid
18 carbons, 3 double bonds 18 carbons, 4 double bonds
Evening primrose, borage and black currant oils
Elongase
Elongase enzyme Elongase enzyme
requires biotin
Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA) Eicosatetraenoic acid
20 carbons, 3 double bonds 20 carbons, 4 double bonds
Liver and other organ meats
Delta-5 desaturase enzyme (D5D) Delta-5 desaturase enzyme (D5D)
arachidonic acid (aa) Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
20 carbons, 4 double bonds 20 carbons, 5 double bonds
Butter, lard, animal fats, brain, organ meats, Fish liver oils, fish eggs
egg yolks, seaweed
Elongase
Elongase enzyme requires biotin Elongase enzyme
Adrenic acid Docosapentaeonic acid
22 carbons, 4 double bonds 22 carbons, 5 double bonds
D6D requires
Delta-6 desaturase enzyme (D6D) Delta-6 desaturase enzyme (D6D)
vitamin B6
Docosapentaenoic acid Docosahexaenoic acid (DHa)
22 carbons, 5 double bonds 22 carbons, 6 double bonds
Human milk, pastured egg yolks, fish liver oils,
fish eggs, liver, brain, organ meats
There are two major types of polyunsaturated fatty acids, those of the omega-6 family and those of the omega-3 fam-
ily. In the body, the eighteen-carbon omega-6 fatty acid linoleic acid (LA) is elongated and made more unsaturated by
enzymes. The key elongated omega-6 fatty acid is arachidonic acid (AA), with twenty carbons and four double bonds;
likewise the eighteen-carbon omega-3 fatty acid, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is elongated and made more unsaturated by
enzymes. The key elongated omega-3 fatty acid is docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). We can also obtain these critical fatty
acids from certain foods, many of which were considered sacred foods by traditional cultures. Too much LA, ALA and EPA
(twenty-carbon omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid) can interfere with the body’s production and utilization of AA and DHA.
Source: Mary G. Enig, PhD, adapted from RR Brenner, PhD, The Role of Fats in Human Nutrition 1989.
20 Wise Traditions FALL 2010