Page 39 - Spring2013
P. 39
investigators determined whether vegetarians with mental disorders began interact with that psychological trait to produce
their vegetarian diet before or after the estimated onset of their mental a disorder. In the German study, half of vegetar-
disorder. ians with eating disorders, two-thirds of those
Compared to omnivores matched for socio-demographic character- with depression, and over 90 percent of those
istics, vegetarians were more than twice as likely to be depressed, more with anxiety disorders developed their mental
than 2.5 times as likely to suffer from an anxiety disorder, and over four disorder before becoming a vegetarian, sug-
times as likely to suffer from an eating disorder. gesting that vegetarianism was not the singular
We could interpret these data in three ways: vegetarianism might “cause” of their mental disorders, at least in the
contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, a pre-existing mental large majority of cases. Nevertheless, as shown
disorder might make someone more likely to become a vegetarian, or an in Figure 1, vegetarianism could have made many
unknown factor might predispose someone both to become a vegetarian of the subjects more likely to be diagnosed with
and to develop a mental disorder. For example, perfectionism is not a men- a mental disorder by aggravating pre-existing
tal disorder and could be beneficial in certain contexts, but the trait could negative psychological traits. In my own case,
contribute to an anxiety disorder if it gets out of hand, and a perfectionist vegetarianism did not “cause” my anxiety dis-
may see vegetarianism as a way of making their diet “perfect.” orders, but it seriously aggravated them, and
These interpretations are not mutually exclusive, however: someone including abundant amounts of nutrient-dense
might be more likely to become a vegetarian because of a particular psycho- animal foods in my diet cured them.
logical trait, but vegetarianism could then induce nutrient deficiencies that We should keep in mind that all eight studies
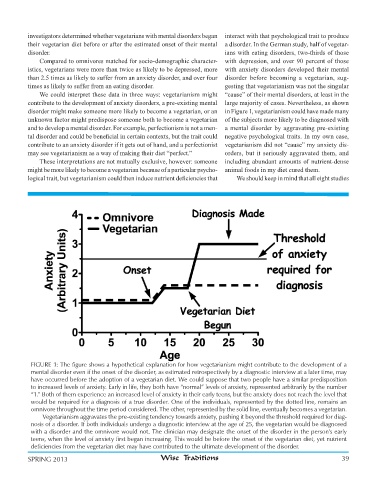
FIGURE 1: The figure shows a hypothetical explanation for how vegetarianism might contribute to the development of a
mental disorder even if the onset of the disorder, as estimated retrospectively by a diagnostic interview at a later time, may
have occurred before the adoption of a vegetarian diet. We could suppose that two people have a similar predisposition
to increased levels of anxiety. Early in life, they both have “normal” levels of anxiety, represented arbitrarily by the number
“1.” Both of them experience an increased level of anxiety in their early teens, but the anxiety does not reach the level that
would be required for a diagnosis of a true disorder. One of the individuals, represented by the dotted line, remains an
omnivore throughout the time period considered. The other, represented by the solid line, eventually becomes a vegetarian.
Vegetarianism aggravates the pre-existing tendency towards anxiety, pushing it beyond the threshold required for diag-
nosis of a disorder. If both individuals undergo a diagnostic interview at the age of 25, the vegetarian would be diagnosed
with a disorder and the omnivore would not. The clinician may designate the onset of the disorder in the person’s early
teens, when the level of anxiety first began increasing. This would be before the onset of the vegetarian diet, yet nutrient
deficiencies from the vegetarian diet may have contributed to the ultimate development of the disorder.
Wise Traditions SPRING 2013 SPRING 2013 Wise Traditions 39